Birds are well known for being important dispersers of many plants, especially via ingested seeds. However, also many other types of organisms may travel attached
Year: 2021
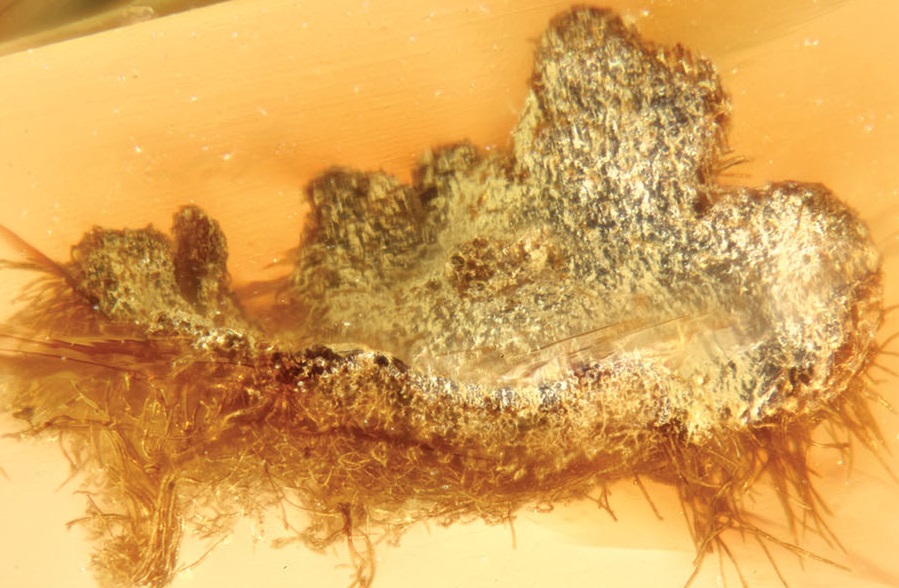

Amber deposits are predominantly known from North America, Europe, and Asia, and are considered to be rare on the continents that formed Gondwana. However, more
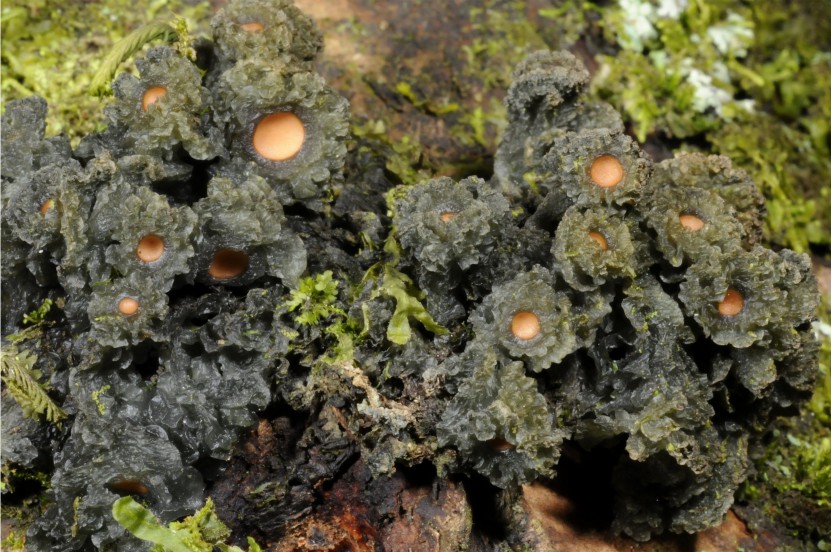

Tropical mountains harbor a wide range of ecosystems, all providing habitats for various sets of organisms, including lichens. For example, the lichens in the savanna
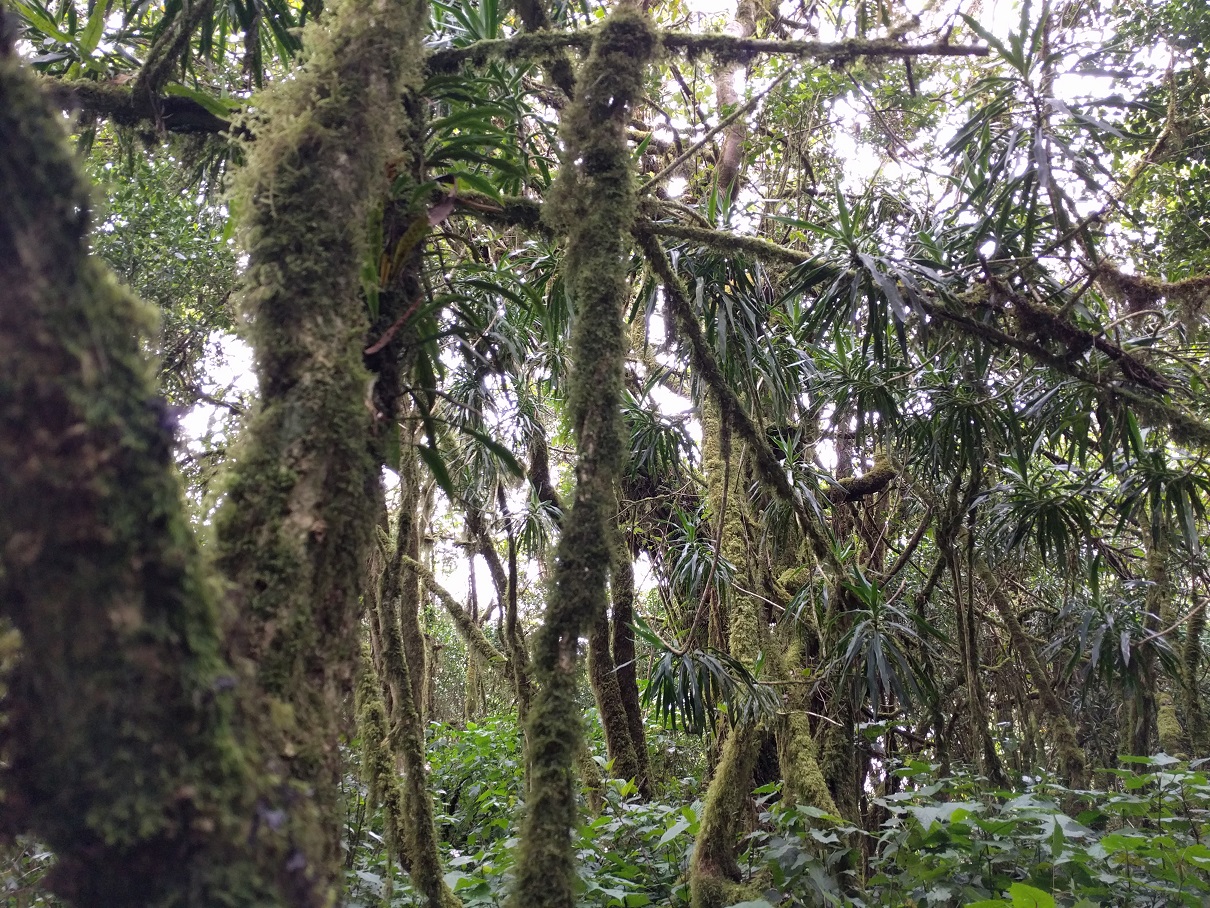

Non-vascular epiphytes, including bryophytes and lichens, have important roles in tropical montane forest ecosystems in intercepting and storing water, nutrient cycling, and providing habitats and
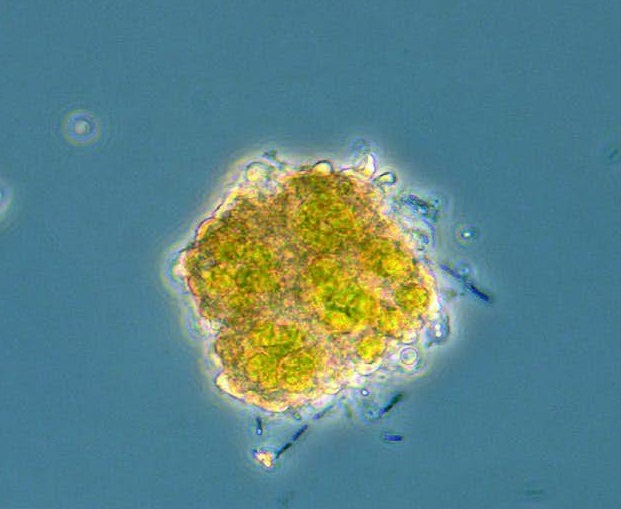
Representatives of the extant lichenized fungal genera Usnea and Ochrolechia and the lichen-inhabiting (lichenicolous) fungus Lichenostigma were already present in the Paleogene amber forests of
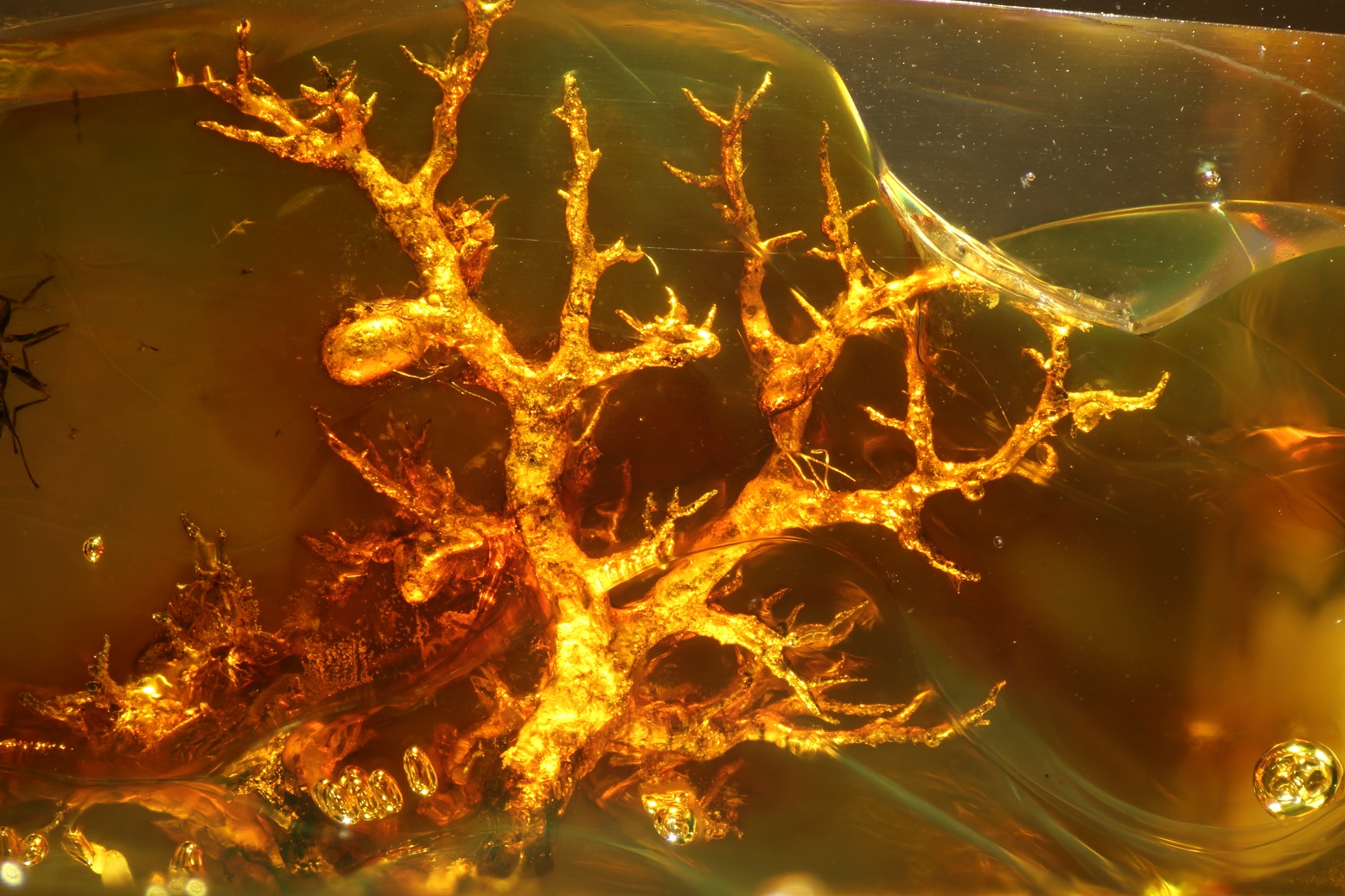
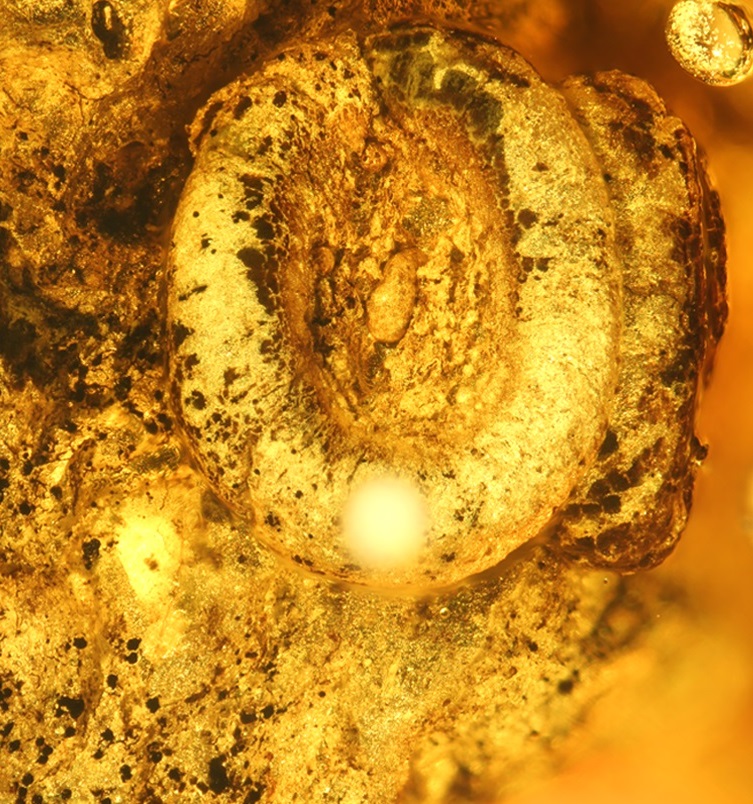
152 new fossil lichens have been discovered from European Palaeogene amber, increasing the total number of known fossil lichens from 15 to 167. Most of
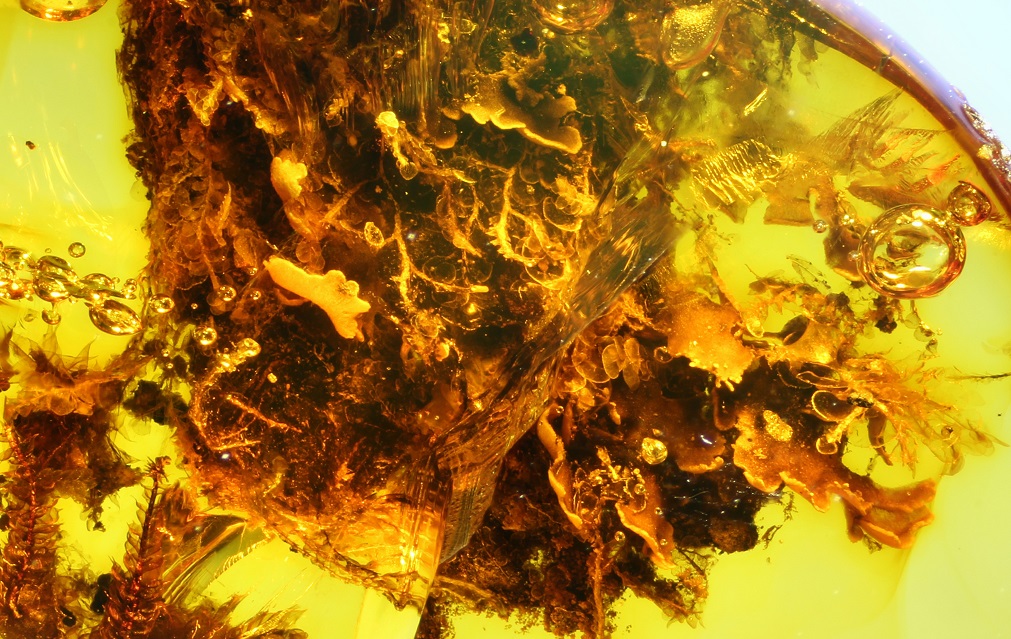

Epiphytes are, for example, vascular plants, bryophytes, or lichens, growing on other plants, like on tree trunks and branches. The diverse epiphytic communities sustain insects
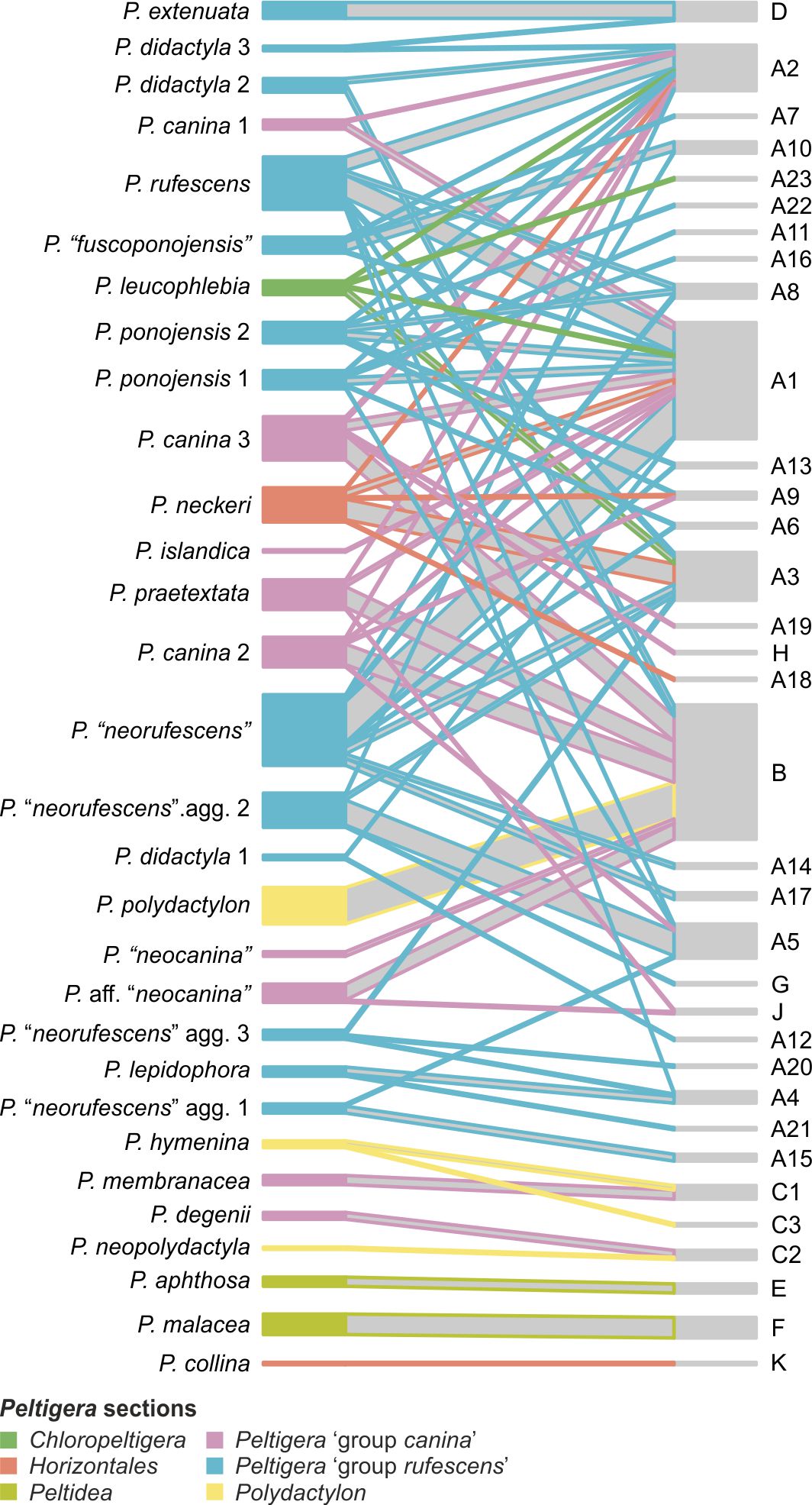
The widespread cyanolichen genus Peltigera (Peltigerales, Lecanoromycetes) comprises many insufficiently known, poorly delimited and/or undescribed species. In Estonia, phylogenetic analyses of Peltigera specimens from a
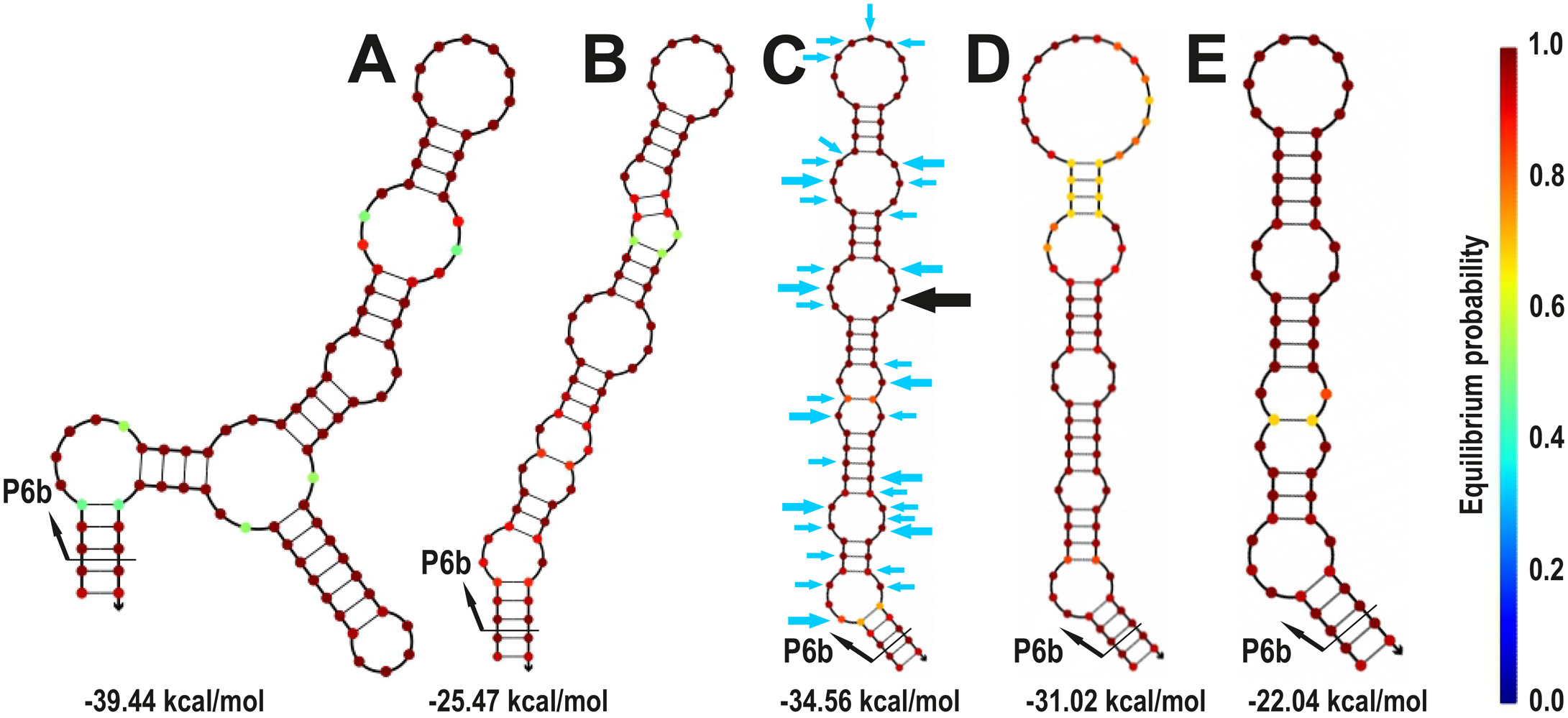
The group I intron interrupting the tRNALeu UAA gene (trnL) is present in most cyanobacterial genomes as well as in the plastids of many eukaryotic
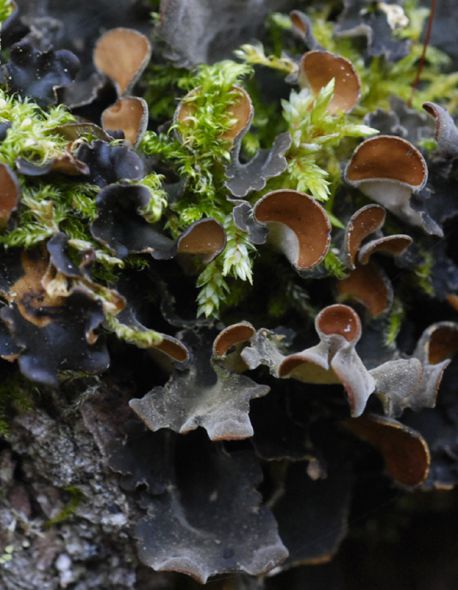

Lichen genus Nephroma (Peltigerales) has a nearly cosmopolitan distribution, and it includes both bipartite species with cyanobacteria as main photobiont as well as cephalodiate species